Understanding Hepatitis B: A Global Health Concern
Hepatitis B is a serious and highly contagious liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV), affecting millions of individuals worldwide. The disease can present as either an acute or chronic condition. If left untreated, it can lead to severe liver damage and life-threatening complications. Raising awareness, promoting preventive strategies, and ensuring timely access to diagnosis and treatment are critical steps in reducing the global burden of hepatitis B.
What Is Hepatitis B?
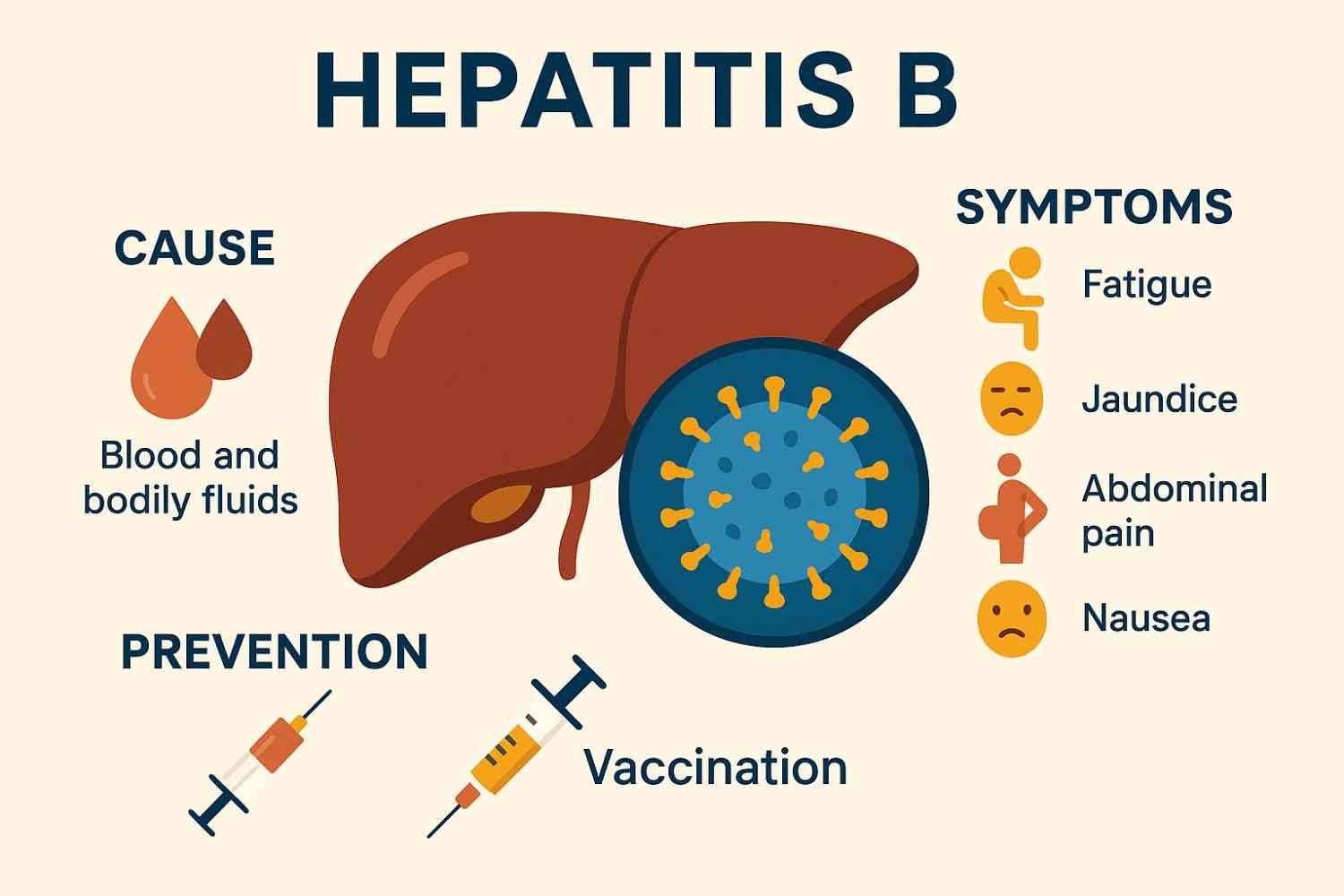
Hepatitis B spreads through contact with infected blood or bodily fluids. Major routes of transmission include unprotected sexual activity, sharing needles or personal hygiene items, and from an infected mother to her baby during childbirth. HBV is a durable virus, capable of surviving outside the human body for extended periods—making early detection and prevention vital.
Health Implications of Hepatitis B
The progression and severity of hepatitis B depend on the type of infection:
-
Acute Hepatitis B: This short-term infection develops soon after exposure. Symptoms may include fatigue, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes). Most healthy individuals recover fully within six months without needing specific treatment.
-
Chronic Hepatitis B: If the virus persists for more than six months, it becomes a chronic condition. This can cause progressive liver damage and significantly increase the risk of cirrhosis, liver failure, and liver cancer. Chronic hepatitis B requires ongoing medical supervision and long-term management.
Prevention Strategies
-
Vaccination: The hepatitis B vaccine is the most effective way to prevent infection. It is safe for all age groups and is particularly important for newborns, healthcare workers, and people at increased risk.
-
Safe Practices: Risk reduction involves practicing safe sex, avoiding the sharing of personal items such as razors or toothbrushes, and ensuring sterile equipment is used for tattoos, piercings, and medical procedures.
Importance of Early Diagnosis
Timely diagnosis is essential, especially for high-risk groups such as healthcare professionals, individuals with multiple sexual partners, and infants born to infected mothers. Blood tests help detect HBV and assess liver function, enabling early intervention and improved treatment outcomes.
Treatment Approaches
-
Acute Infections: Typically, supportive care—including rest, hydration, and monitoring—is sufficient, as the body’s immune system can usually eliminate the virus.
-
Chronic Infections: Long-term management involves antiviral medications that help suppress the virus and reduce liver inflammation. Regular medical checkups and healthy lifestyle choices are crucial to maintaining liver health and preventing complications.
Addressing the Global Burden
Hepatitis B remains a pressing public health issue, especially in regions with limited access to healthcare. Expanding immunization coverage, increasing awareness, and ensuring availability of diagnostic and treatment services are fundamental to reducing the disease’s global impact.
Ensuring Access to Essential Medications
For individuals living with chronic hepatitis B, continuous access to effective antiviral treatments is vital. Reliable pharmaceutical supply chains—especially trusted exporters of medications such as Entavir (Entecavir)—are key to supporting global treatment efforts. Strengthening these networks ensures consistent medication availability, promotes ongoing patient care, and contributes to improved health outcomes across communities.

