Understanding Hepatitis B: A Global Health Concern
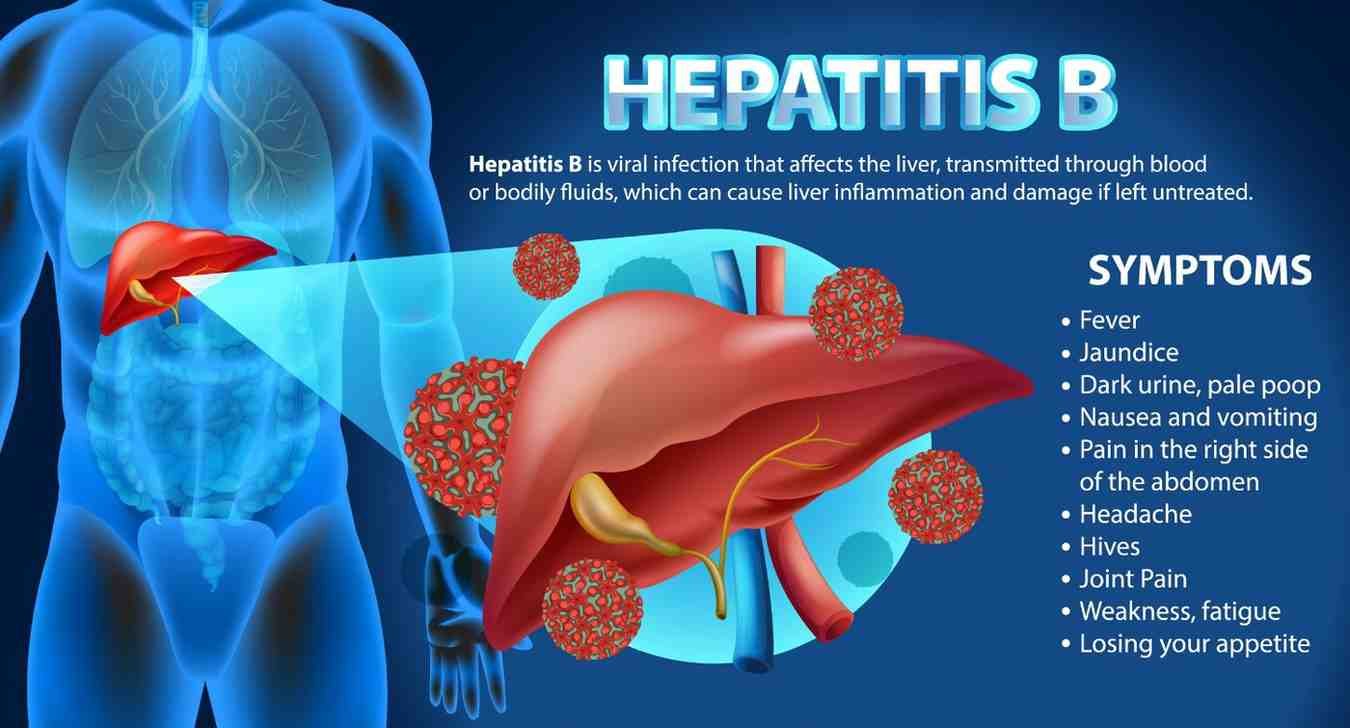
Hepatitis B is a widespread viral infection with serious implications for global health, affecting millions of individuals worldwide. Caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV), this potentially severe liver disease can present in both acute and chronic forms. A thorough understanding of Hepatitis B is essential for effective prevention, diagnosis, and management, emphasizing its impact and necessary interventions.
Defining Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that primarily targets the liver. It spreads through contact with infected blood, unprotected sexual encounters with an infected person, or transmission from an infected mother to her newborn during childbirth. Due to the virus’s ability to survive outside the body, it remains highly contagious, making awareness and preventive measures crucial.
The Impact
Hepatitis B can range from a mild illness to a chronic, life-threatening condition. Acute symptoms may include fatigue, jaundice, abdominal pain, and nausea, typically resolving within a few months. However, if the virus persists beyond six months, it can lead to chronic Hepatitis B, which increases the risk of liver damage, cirrhosis, and liver cancer over time.
Prevention
- Vaccination: The most effective preventive measure is vaccination. The HBV vaccine is safe, widely available, and recommended for all age groups, particularly infants and individuals at high risk due to their occupations or lifestyles.
- Safe Practices: Reducing the risk of transmission involves practicing safe sex, using sterile needles and equipment for tattoos, piercings, and medical procedures, and avoiding sharing personal items like razors or toothbrushes.
Diagnosis
Early detection is vital for managing Hepatitis B effectively. Blood tests are the primary diagnostic tool, helping identify the virus and assess liver function. Testing is particularly recommended for high-risk individuals, including healthcare workers, those with multiple sexual partners, and individuals born to infected mothers.

Treatment
- Acute Hepatitis B: Treatment primarily involves supportive care, including rest, adequate hydration, and close monitoring. In most cases, the immune system clears the infection within six months.
- Chronic Hepatitis B: Long-term cases may require antiviral medications to suppress the virus and reduce the risk of liver complications. Regular monitoring and lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing the condition effectively.
Global Impact
Hepatitis B is a significant global health challenge, particularly in regions with limited access to healthcare and vaccination programs. Efforts focused on increasing awareness, expanding vaccination campaigns, and improving access to testing and treatment are essential in reducing the disease burden worldwide.
Conclusion
Addressing Hepatitis B requires a comprehensive approach that includes prevention, early detection, and effective treatment strategies. For those managing the condition, partnering with a reliable Entavir Entecavir Hepatitis B bulk cargo exporter can ensure access to quality medications, contributing to better disease management and improved health outcomes.

